Depressed people who reflexively try and dampen their preliminary emotional responses to reminders of their adverse reminiscences have a low tolerance for distressing emotional stimuli normally and will reply to stress of their every day lives with higher upticks in suicidal ideas. A brand new research in Organic Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, printed by Elsevier, examined the connection of the engagement of emotion regulation to real-world responses to emphasize to be able to higher perceive stress-related will increase in suicide danger in melancholy.
Suicide charges in the USA have elevated about 37% because the 12 months 2000. To reverse this development, we have to perceive how suicide danger emerges in every day life, and particularly the biopsychosocial components which will affect the ebb and move of suicide danger.”
J. John Mann, MD, Molecular Imaging and Neuropathology Division, New York State Psychiatric Institute
Retrospective stories present that probably the most fast set off of suicidal acts is a aggravating life occasion, however researchers say it is extremely tough to prospectively research how stress impacts the emergence of acute suicidality.
Co-first writer Sarah Herzog, PhD, Molecular Imaging and Neuropathology Division, New York State Psychiatric Institute; and Division of Psychiatry, Columbia College Vagelos School of Physicians and Surgeons, explains, “Ecological momentary evaluation permits us to watch how people affected by melancholy react to aggravating occasions of their every day lives, for instance, with intensified suicidal ideas and worsened temper. Our research took this a step additional by linking a laboratory-based organic marker of danger in a depressed pattern to naturalistic responses to real-world every day stressors. This multimodal technique prmoises to enhance prediction of suicide danger in these susceptible to suicide and maybe aiding efficient intervention of probably life-threatening reactions to emphasize.”
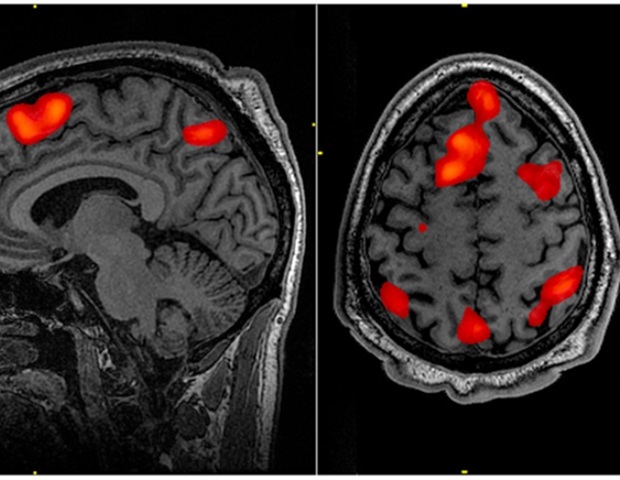
A bunch of 82 contributors with main depressive dysfunction was assessed utilizing two revolutionary strategies. First, a useful MRI (fMRI)-based neural signature for cognitive reappraisal, an emotion regulation technique, quantified the diploma to which people engaged emotion regulation whereas recalling private adverse reminiscences. Subsequent, researchers used ecological momentary evaluation (EMA), which entails potential, repeated measurement of contributors’ ideas and feelings in naturalistic settings. EMA gives a window into how people react to every day life stressors with modifications in temper signs and suicidal ideas. The researchers then used the fMRI-based neural signature of emotion regulation expressed throughout the autobiographical reminiscence job to foretell contributors’ responses to every day life stressors throughout the EMA interval.
The research discovered that depressed people who spontaneously engaged a neural signature of emotion regulation when introduced with private adverse reminiscences additionally skilled higher will increase in suicidal ideas throughout day-to-day aggravating occasions over the course of per week. When contributors had been directed to make use of reappraisal, they confirmed extra adaptive responses to emphasize.
Editor-in-Chief of Organic Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging Cameron S. Carter, MD, College of California Irvine, feedback, “Flexibility in emotion regulation is mostly understood to be a marker of psychological well being. Nonetheless, within the present research researchers discovered that reflexively participating emotion regulation within the face of surprising stressors is probably not useful or efficient in all circumstances. These findings, which leverage useful imaging mixed with real-world within the second assessments, are essential to additional our understanding of tips on how to successfully cope with stress in every day life.”
Co-first writer Noam Schneck, PhD, Molecular Imaging and Neuropathology Division, New York State Psychiatric Institute; and Division of Psychiatry, Columbia College Vagelos School of Physicians and Surgeons, factors out, “The usage of neural decoding permits us to determine psychological processes that had been beforehand elusive to seize, akin to spontaneous emotion regulation. In future work, the decoder strategy will be employed to higher perceive how emotion regulation is engaged spontaneously to modulate hour-to-hour, day-to-day expertise, thereby influencing suicide danger in a fluctuating method.”
Senior writer of the present research Barbara H. Stanley, MD, Molecular Imaging and Neuropathology Division, New York State Psychiatric Institute; and Division of Psychiatry and Division of Radiology, Columbia College Vagelos School of Physicians and Surgeons, who handed away in 2023, was instrumental in designing this research. Recognizing her worthwhile contributions to this work, Dr. Mann remarks, “It was Dr. Stanley’s concept that we make use of ecological momentary evaluation in the identical depressed sufferers who accomplished the fMRI adverse autobiographical reminiscences job. It was that mixture of analysis procedures that led to those outstanding findings.”