This week, the federal authorities introduced it can pay states and territories an additional, one-off, A$1.7 billion for public hospitals.
This has been billed as a strategy to repair some ailing hospitals, and shorten waits for care in emergency departments and for elective surgical procedure. However will it actually make a distinction?
How are hospitals funded?
Australian public hospitals are funded via a collaborative association involving state, territory and federal governments. The federal authorities gives 37% of public hospital funding yearly, primarily via the Nationwide Well being Reform Settlement. States and territories fund practically all the remaining.
Most federal authorities funding for public hospitals is decided by an “exercise based mostly funding” components. Funding is predicated on the variety of sufferers handled and the worth of remedy, the latter calculated from common public hospital prices.
State and territory governments handle public hospitals. The federal authorities has little say on how public hospital cash is spent. The exception is when funding pertains to one thing particular, like a brand new hospital ward.
How the additional funding compares
The federal authorities will spend $30.19 billion on public hospitals this monetary yr. The additional funding will develop its public hospital spending by 12% in 2025–26.
Additional funding will probably impression Northern Territory hospitals probably the most. It’ll obtain $51 million extra, a 30% improve.
Whereas bigger states will obtain extra funding, they’ve extra public hospitals and sufferers. For instance, New South Wales will obtain $407 million, however this equates to solely an 11% improve from the federal authorities.
The additional funding is much less spectacular when in comparison with complete public hospital spending. That was $86 billion in 2022–23, suggesting the additional $1.7 billion will characterize lower than 2% in extra complete funding to public hospitals in 2025–26.
However this further spending shouldn’t be in isolation. The federal authorities has already dedicated practically $600 million to ascertain 87 pressing care clinics round Australia. Their major function is to alleviate strain on emergency departments and fill gaps in entry to after-hours major care.

khuncho24/Shutterstock
Stress in public hospitals
Public hospital strain has been constructing for over a decade. Emergency departments are sometimes clogged, resulting in lengthy wait instances, largely due to employees shortages. Round 10% of sufferers wait greater than two hours. There’s little slack within the system to counter unpredictable surges in demand for care.
The proportion of emergency division sufferers seen on time has declined since COVID. The proportion of sufferers requiring pressing emergency division care seen on-time, for instance, has decreased from 67% to 61%. Extra non-urgent and semi-urgent sufferers are additionally not receiving care on time.
Sufferers are additionally ready longer for elective public hospital surgical procedure since COVID, regardless of a rise within the variety of admissions from elective surgical procedure ready lists.
Proportion of sufferers seen on time in public hospital emergency departments
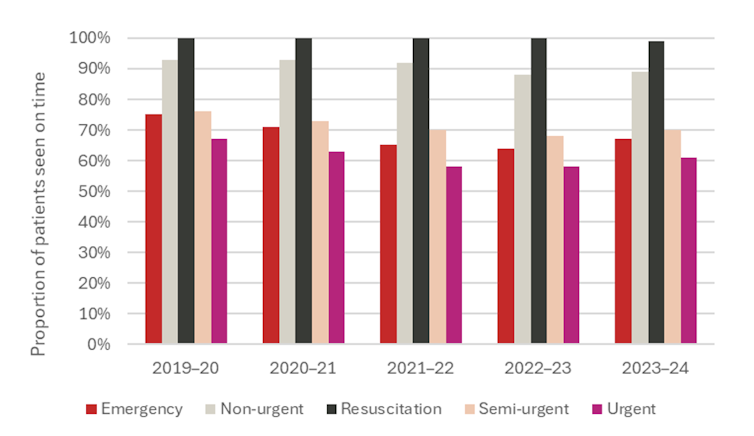
Australian Institute of Well being and Welfare
Ready instances fluctuate by state and territories. Queensland has the lowest proportion of sufferers ready greater than three hundred and sixty five days for public hospital elective surgical procedure at 3.9% in 2023–24, whereas the ACT had the very best at 8.9%.
Encouragingly, ready instances decreased for practically all elective surgical procedures in comparison with 2022–23, suggesting public hospitals could also be making inroads into the post-COVID load.
Proportion of sufferers ready greater than three hundred and sixty five days for public hospital elective surgical procedure
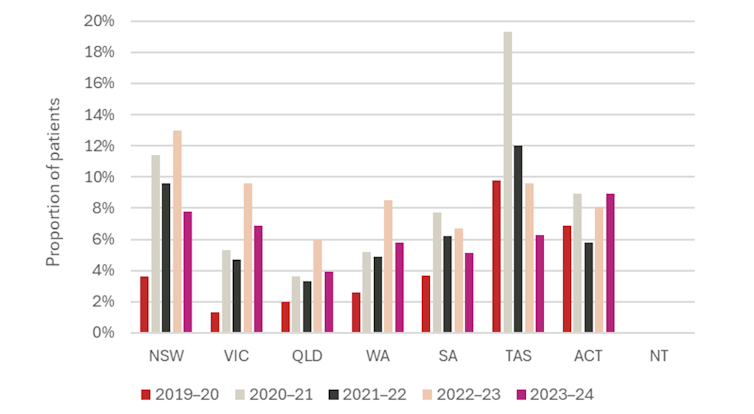
Australian Institute of Well being and Welfare
Will the cash assist?
Whereas extra funding will assist, there is no such thing as a magic wand. Public hospitals have to considerably reorganise their employees, workflows, beds and buildings. This in an atmosphere that has workforce shortages, burnout, and wage pressures, making main well being system adjustments notably troublesome.
Some hospitals might cut back their ready instances considerably, if states and territories allocate their further funding to poor performers.
Nonetheless, poor efficiency will be associated to systemic points out of the hospital’s management, akin to workforce shortages. With out a rise in complete health-care workforce dimension, these poor performing hospitals might search for extra employees from different public hospitals, worsening their efficiency.
Whether or not any enhancements final is one other query.
Public hospitals face elevated demand for emergency division care, solely mitigated by the potential success of pressing care clinics.
Learn extra:
Labor’s pressing care centres are a step in the appropriate route – however not a panacea
Public hospitals additionally face a rise in demand for elective surgical procedure, because the inhabitants ages and power illness prevalence will increase.
The additional $1.7 billion is just a one off. Funds to scale back ready instances will largely be spent on extra employees, akin to nurses, clinicians and administration employees.
Public hospitals will want extra, ongoing funding to maintain up with demand, in any other case any preliminary enchancment will dissipate.

Gorodenkoff/Shutterstock
What else must occur?
All governments want to take a position extra in prevention applications to gradual the expansion in public hospital demand.
Extra Australians are overweight, as a proportion of the inhabitants, in comparison with different OECD international locations. This has created a heavy burden.
Decreasing monetary waste within the health-care system is of big significance. Financial savings may very well be used for long-term enhancements in ready instances as soon as the additional funding runs out.
Round 40% of well being care is of low worth or causes hurt. Decreasing pointless medical exams, rushing up discharges, and decreasing avoidable admissions is an effective begin.
Different adjustments that might assist embody:
- setting nationwide efficiency targets for states and territories to scale back their ready lists
- stronger monitoring of efficiency
- holding public hospital managers extra accountable for reaching their ready time targets.
A brand new Nationwide Well being Reform Settlement is because of take impact in 2026. Whoever wins this yr’s federal election must finalise this settlement with the states and territories.
The Commonwealth and states are but to decide to all the suggestions from the mid-term overview of the present settlement launched in October 2023. The extent to which governments settle for these suggestions has the potential to create a a lot better, long-term impression on ready instances than this further, one-off cost.

